This is a continuous process in which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back again.
Water Cycle
This powers the water cycle
The Sun
The sun's energy changes water from a liquid to a gas during this part of the water cycle
Evaporation
During this part of the water cycle, the atmosphere cools down the water vapor and changes it back to a liquid
Condensation
During this part of the water cycle water falls back to Earth's surface once large enough droplets have formed
precipitation
Types of this are rain, snow, sleet, or hail
precipitation
During this part of the water cycle, water is a liquid
Condensation
During this part of the water cycle, water is a gas
Evaporation
This is the condition of the atmosphere at a given place and time
Weather
This heats and cools faster than water
Land
These can also affect air temperature; during the day they may reflect the sun's rays away from the Earth making the air cooler. And at night they may keep the heat from the sun trapped close to the surface
Clouds
This is the weight of the air pushing down and is measured with a barometer
air pressure
As the altitude increases air pressure...
Decreases
This is the amount of water vapor in the air; it's measured with a hygrometer
humidity
_____ air can hold more water vapor than ____ air.
Warm, cold
When the humidity is ______, the air is drier.
Low
How fast or slow the wind is blowing is called _____
Wind Speed
Where the wind is coming from and going to is called ______
Wind Direction
The speed and direction of the wind can affect the _____ in an area.
Weather
If the wind is traveling from over ______ it will be drier.
Land
If wind is traveling from over ______ it will be wetter, containing more water vapor.
Water
Type of precipitation that is a liquid and occurs at 33 degrees or warmer.
Rain
Type of precipitation that is a solid and occurs at 32 degrees or colder.
Snow
Type of precipitation that is a solid/liquid mix and forms when rain travels through a freezing layer of air.
Sleet
Type of precipitation that is a solid and forms during a storm when strong upward winds whip rain into the freezing temperatures in the upper atmosphere.
Hail
These form when water vapor cools down and changes state from a gas to a liquid.
Clouds
What type of clouds are these?
Stratus

These high clouds are made of ice.
Cirrus
These fluffy, white cotton ball clouds signal fair weather.
Cumulus
What type of clouds are these?
Cumulonimbus

These clouds can cover the whole sky. They are also fog clouds.
Stratus
These clouds are dark, puffy, tall storm clouds that are dark gray in color.
Cumulonimbus
What type of clouds are these?
Cumulus

What type of clouds are these?
Cirrus

This is the average weather in an area over a long period of time (more than 30 years).
Climate
This can affect climate and is the distance North or South of the Equator.
Latitude
The closer you get to the equator, the ______ the temperatures.
hotter
Identify the climate zone in yellow.
Tropical
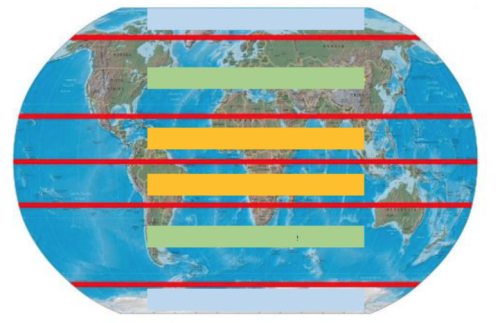
Identify the climate zone in green.
Temperate
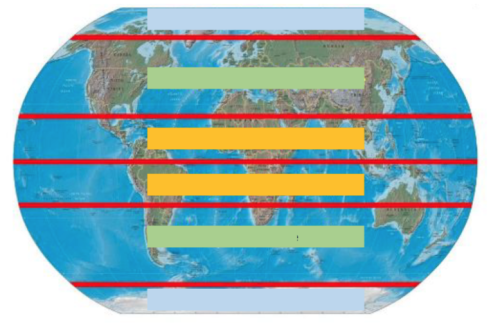
Identify the climate zone in blue.
Polar
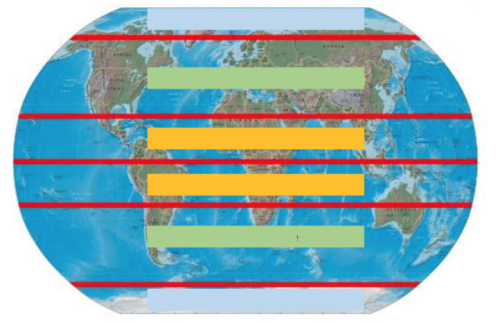
This climate zone does not get direct sunlight any time during the year causing temperatures to be cold all year long.
Polar
These zones get direct sunlight all year long causing the temperatures to be warm all year long. This zone also receives the most rainfall because the warm weather leads to a lot of evaporation.
Tropical
This zone has hot summers and cold winters. The amount of direct sunlight changes throughout the year because of the tilt of the Earth's axis.
Temperate
This is the height of an area above sea level.
Elevation
The top of a mountain is generally ______ than the bottom of a mountain.
colder
Higher elevations have ______ air pressure.
lower
The temperature of water changes much more ____ than the temperature of land.
slowly
This environment has year round heat and humidity; it's wet all the time. This environment is often located in tropical areas
swamp/wetlands
This environment has very little precipitation; it is hot in the daytime and cold at night. It also has low humidity.
Desert
This environment is the coldest and driest of all areas; it has long winders and short summers. It stays cold all year.
Tundra
This environment has a rainy season and generally has warm summers and cold winters. It is found between forests and deserts.
grassland
This environment is warm all year. It has very high humidity and high amounts of rainfall each year.
Tropical Rainforest





